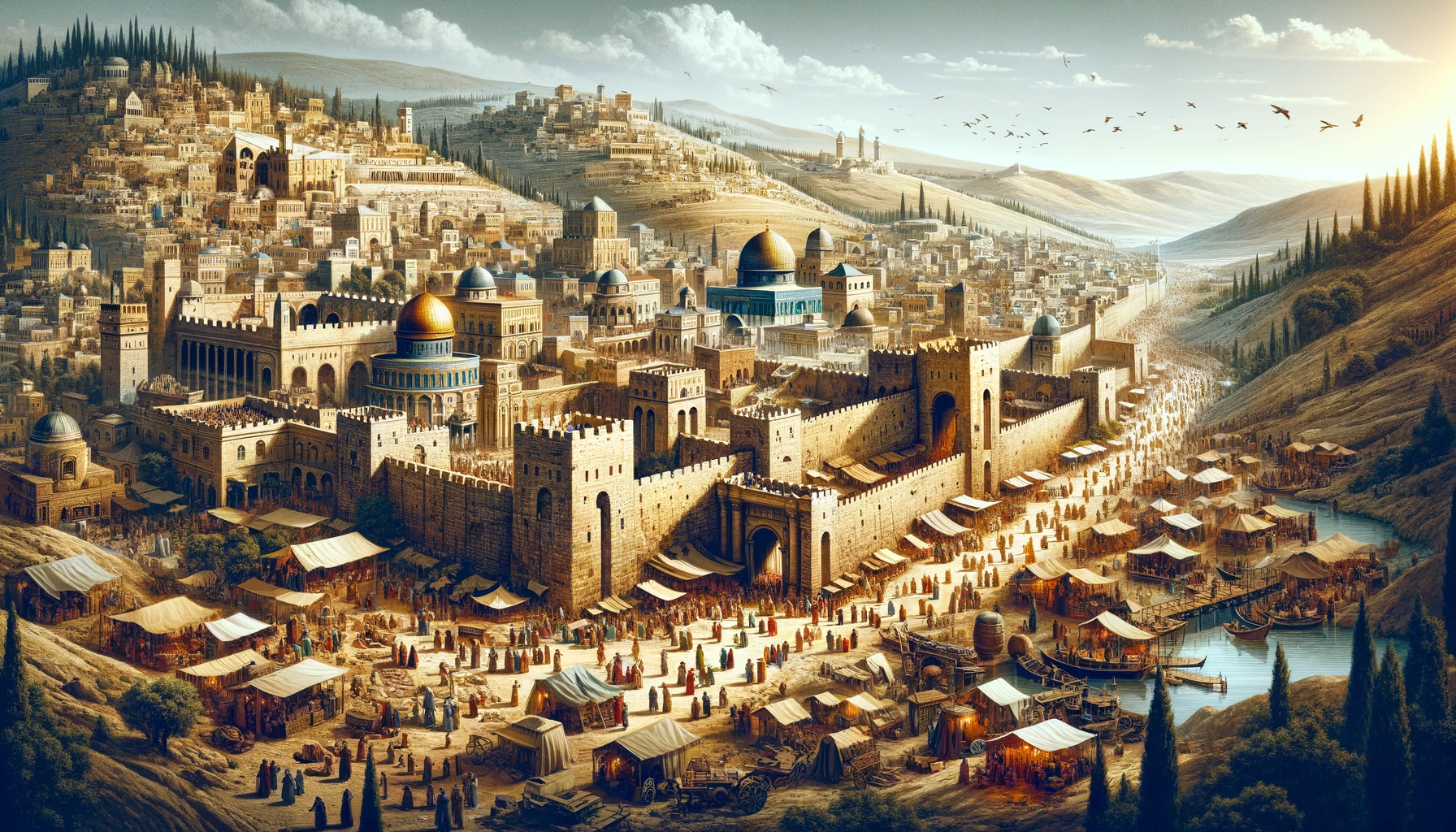
Have you ever wondered what life was like in ancient Jerusalem during 30 A.D.?
Imagine walking the bustling streets of a city steeped in history, where every corner tells a story of faith, conflict, and innovation.
What secrets do the stones of Jerusalem hold?
How did the residents of this historic city balance their daily routines with the spiritual significance of their surroundings?
Join us as we delve into the heart of ancient Jerusalem, exploring the marvels of its architecture, the significance of its key locations, and the pulse of its streets, where the past and present intertwine to tell a story like no other. Discover the wonders of a city that stood as a beacon of culture, religion, and ingenuity in a time that shaped the course of history.
Sermon Bulletpoints
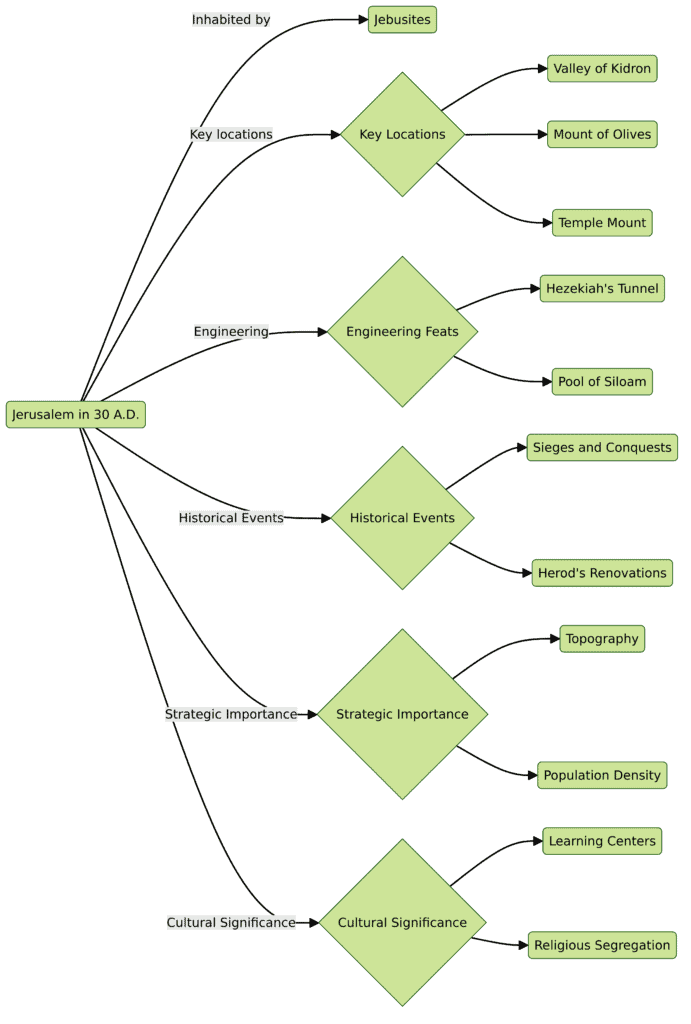
- 🏰 Ancient Jerusalem: Originally inhabited by the Jebusites, Jerusalem’s strategic and religious significance evolved over centuries.
- 📜 Biblical References: Key locations like the Valley of Kidron, Mount of Olives, and the Temple Mount are pivotal in biblical narratives.
- 🛠️ Engineering Feats: Hezekiah’s tunnel and the Pool of Siloam are examples of advanced ancient engineering.
- 🕍 Temple Complex: The Temple Mount expanded under various rulers, serving as a central worship site for Jews.
- ⚔️ Sieges and Conquests: Jerusalem faced numerous attacks and changes in rulership, affecting its structure and population.
- 🏗️ Herod’s Renovations: Herod the Great significantly enhanced Jerusalem’s architecture, including the temple and his palace.
- 🗺️ Strategic Topography: Jerusalem’s hills, valleys, and location influenced its historical and military significance.
- 🚪 Access Controls: The Soreg separated the Court of the Gentiles from the inner temple courts, indicating strict religious boundaries.
- 📚 Learning Centers: The temple’s porticos were hubs for business, education, and religious discussions.
- 🛤️ Population and Size: Estimates vary, but Jerusalem was densely populated, especially during significant festivals like Passover.
Visual Representation Of What You Will Learn In This Sermon
Can Understanding Jerusalem’s History Help Explain the Israel-Palestine Conflict?
Understanding Jerusalem’s history is crucial in tracing the Israel-Palestine conflict. The city holds deep religious and cultural significance for both Israelis and Palestinians. Its complex past, including years of conquest and religious rivalry, has contributed to the ongoing conflict over the territory.
What Role Did Jerusalem Play in the Parable of the Ten Virgins from Matthew 25?
Jerusalem is not specifically mentioned in the Parable of the Ten Virgins in Matthew 25, but it is a central location for understanding the context of the parable. In Matthew 25, the keyword “unveiling mysteries Matthew 25” highlights the deeper meaning behind the parable and its relevance to the end times.
Summary
- The tour provides an immersive view of Jerusalem in 30 A.D., focusing on historical and biblical contexts.
- Jerusalem’s early inhabitants, the Jebusites, were eventually overtaken by tribes of Israel, setting the stage for its evolution.
- Significant biblical locations like the Valley of Kidron and Mount of Olives are highlighted, illustrating their importance in ancient narratives.
- The engineering marvels of Hezekiah’s tunnel and the Pool of Siloam demonstrate the advanced infrastructure of the time.
- The Temple Mount, central to Jewish worship, underwent various expansions and renovations, reflecting its importance through different eras.
- Herod the Great’s architectural contributions significantly shaped Jerusalem’s landscape, including the temple and his palace.
- The city’s geography, including its hills and valleys, played a crucial role in its history and strategic defense.
- Regulations like the Soreg underscored the strict religious segregation and practices within the temple complex.
- The porticos around the temple served multiple functions, including education, business, and religious discourse.
- Despite its compact size, Jerusalem’s population swelled during major festivals, underscoring its central role in Jewish religious life.
Affiliate Disclosure: "As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases made from links in this post. We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com."

